Dysphagia can be caused by innumerable disease processes. It has a significant impact on quality of life, life expectancy, and the utilization of health care resources. The most common causes of dysphagia have not been previously clarified. UC Davis CVS researchers led by Dr. Belafsky have published work that has documented the most common causes of swallowing difficulty in outpatient dysphagia sufferers (Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2013 May;122(5):335-8.).
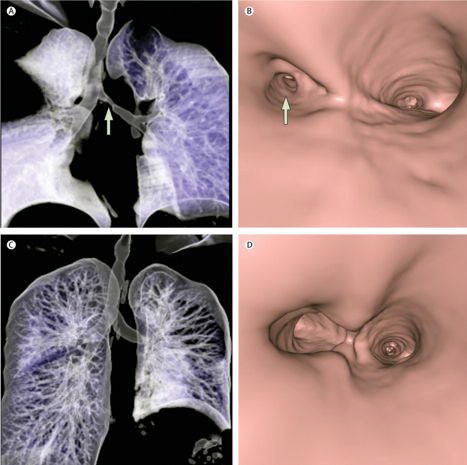
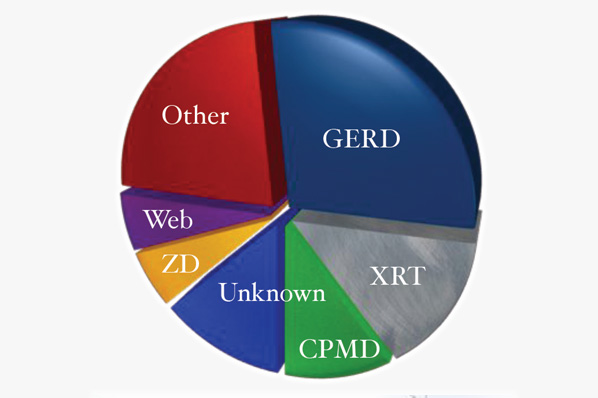
Gastroesophageal reflux was the most common cause of swallowing impairment followed by radiation treatment for head and neck cancer and cricopharyngeus muscle dysfunction. Other less common causes of dysphagia identified by our team include esophageal dysmotility, progressive neurologic disease, hiatal hernia, eosinophilic esophagitis, vocal fold immobility, cervical spine surgery, and achalasia.
Interestingly, despite the most contemporary state-of-the-art diagnostic equipment, a source of the swallowing
complaint could not be identified in 13% of individuals. This highlights the need to differentiate between the subjective symptom of dysphagia and objective evidence of swallowing impairment and identifies room for improvement in our ability to diagnose tertiary causes of dysphagia.
These findings allow clinicians to better allocate health care resources and focus their research efforts to areas that provide maximum patient benefit and quality of life improvement.